- Digital Communication Tutorial
This tutorial video will show how to draw basic modulation techniques for amplitude-shift keying (ASK), frequency-shift keying (FSK) and phase-shift keying (. Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands.
- Digital Communication Resources
- Selected Reading
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) is a type of Amplitude Modulation which represents the binary data in the form of variations in the amplitude of a signal.
Any modulated signal has a high frequency carrier. The binary signal when ASK modulated, gives a zero value for Low input while it gives the carrier output for High input.
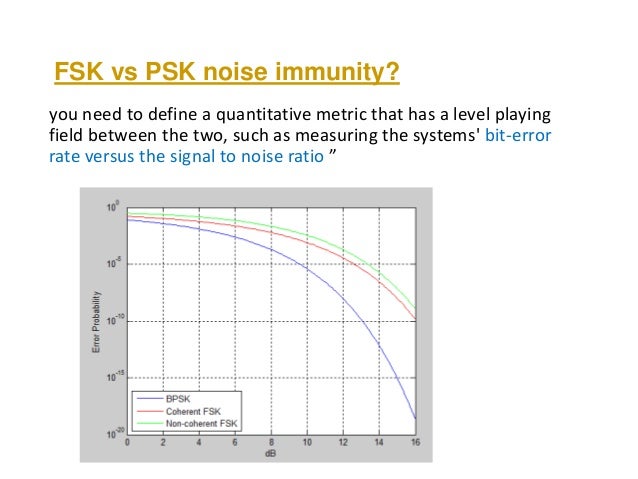
- ASK, PSK and FSK are signaling schemes used to transmit binary sequences through free space. In these schemes, bit-by-bit transmission through free space occurs. FSK (Frequency Shift Keying): In FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) binary 1 is represented with a high-frequency carrier signal and binary 0 is represented with a low-frequency carrier, i.e.
- This post discusses Digital Modulation Techniques (ASK, FSK and PSK). The Waveforms, Definition and Basic Concepts of each digital modulation Techniques are discussed here. You will find here the basic difference between digital modulation and analog modulation. The digital modulation techniques are amplitude shift keying (ASK), frequency shift keying (FSK) and Phase shift keying (PSK).
The following figure represents ASK modulated waveform along with its input.
To find the process of obtaining this ASK modulated wave, let us learn about the working of the ASK modulator.
ASK Modulator
The ASK modulator block diagram comprises of the carrier signal generator, the binary sequence from the message signal and the band-limited filter. Following is the block diagram of the ASK Modulator.
The carrier generator, sends a continuous high-frequency carrier. The binary sequence from the message signal makes the unipolar input to be either High or Low. The high signal closes the switch, allowing a carrier wave. Hence, the output will be the carrier signal at high input. When there is low input, the switch opens, allowing no voltage to appear. Hence, the output will be low.
The band-limiting filter, shapes the pulse depending upon the amplitude and phase characteristics of the band-limiting filter or the pulse-shaping filter.
ASK Demodulator
There are two types of ASK Demodulation techniques. They are −
Ask Fsk Psk Qam
- Asynchronous ASK Demodulation/detection
- Synchronous ASK Demodulation/detection
The clock frequency at the transmitter when matches with the clock frequency at the receiver, it is known as a Synchronous method, as the frequency gets synchronized. Otherwise, it is known as Asynchronous.
Asynchronous ASK Demodulator
The Asynchronous ASK detector consists of a half-wave rectifier, a low pass filter, and a comparator. Following is the block diagram for the same.
The modulated ASK signal is given to the half-wave rectifier, which delivers a positive half output. The low pass filter suppresses the higher frequencies and gives an envelope detected output from which the comparator delivers a digital output.
Synchronous ASK Demodulator
Synchronous ASK detector consists of a Square law detector, low pass filter, a comparator, and a voltage limiter. Following is the block diagram for the same.
The ASK modulated input signal is given to the Square law detector. A square law detector is one whose output voltage is proportional to the square of the amplitude modulated input voltage. The low pass filter minimizes the higher frequencies. The comparator and the voltage limiter help to get a clean digital output.
PSK Advantages | PSK Disadvantages | Phase Shift Keying
This page covers advantages and disadvantages of PSK. It mentions PSK advantages or benefits and PSK disadvantages or drawbacks.PSK stands for Phase Shift Keying.
What is PSK?
Introduction:
It is a digital modulation technique which uses phase of the analog carrierto represent digital binary data. Phase of the carrier wave is changed according tothe binary inputs (1 or 0). In two level PSK, difference of 180 phase shift is usedbetween binary 1 and binary 0.
There are many different types of modulation techniques which utilizesthis concept to transmit digital binary data. It include two level PSK (i.e. BPSK),Four level PSK (i.e. QPSK) etc. Some techniques employ both amplitude andphase variation to represent binary data such as 16-QAM, 64-QAM, 256-QAM etc.Two level PSK represents single bit by each signaling elements whilefour level PSK represents two bits by each signaling elements and so on.8-PSKrepresents three bits by each signaling elements.
Following are the equations used to represent BPSK.
➨s(t) = A*cos(2*π*fc*t) for Binary 1 than
➨s(t) = A*cos(2*π*fc*t + π) for Binary 0
Refer difference between ASK vs FSK vs PSK >> andBPSK vs QPSK>> for more information.
As mentioned there are many variants of PSK modulation.Each of these PSK types have different advantages and disadvantages.We will have a look at common advantages and disadvantages of PSK techniques.One can also refer advantages and disadvantages ofBPSK modulation >>,QPSK modulation >> andQAM modulation >>.
Benefits or advantages of PSK
Following are the benefits or advantages of PSK:
➨It carries data over RF signal more efficiently compare to other modulation types.Hence it is more power efficient modulation technique compare to ASK and FSK.
➨It is less susceptible to errors compare to ASK modulation andoccupies same bandwidth as ASK.
➨Higher data rate of transmission can be achieved using high level of PSKmodulations such as QPSK (represents 2 bits per constellation), 16-QAM (represents 4 bits per constellation) etc.
Drawbacks or disadvantages of PSK
Ask Fsk Psk Comparison
Following are the disadvantages of PSK:
➨It has lower bandwidth efficiency.
➨The binary data is decoded by estimation of phase states of the signal.These detection and recovery algorithms are very complex.
➨Multi-level PSK modulation schemes (QPSK, 16QAM etc.) are more sensitive to phase variations.
➨It is also one form of FSK and hence it also offers lower bandwidthefficiency compare to ASK modulation type.
Also refer advantages and disadvantages ofASK Modulation >> andFSK Modulation >>.
Modulation types
AM vs FM vs PM
AM FM PM MATLAB Code
What is modulation
BPSK-This page describes BPSK modulation technique with equation and constellation diagram.
QPSK -This page describes QPSK modulation technique with equation and constellation diagram.
QAM-This page describes QAM modulation technique with equation and constellation diagram.
MSK-GMSK MSK modulation,GMSK modulation and GMSK demodulation.
8PSK 8-PSK modulation or multilevel PSK or phase shift keying modulation technique.
BPSK vs QPSK -Difference Between BPSK and QPSK modulation techniques.
QPSK vs OQPSK vs pi/4QPSK-Difference between QPSK,OQPSK and pi/4QPSK modulation techniques
Differential Encoder and Decoder
Advantages and Disadvantages of other wireless technologies
What is Difference between
difference between OFDM and OFDMA
Difference between SC-FDMA and OFDM
Difference between SISO and MIMO
Difference between TDD and FDD
FDMA vs TDMA vs CDMA
FDM vs TDM
CDMA vs GSM